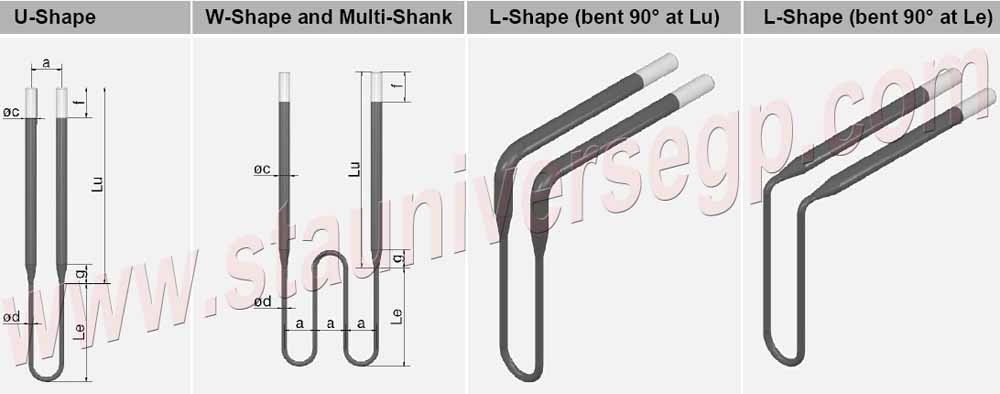
The Multi-Shank MoSi2 heating element is a dense cermet material consisting of MoSi2 and an oxide, glassy phase component. It is have more heating zone compare with U type MoSi2 heater.
The Multi-Shank MoSi2 heating element is a dense cermet material consisting of MoSi2 and an oxide, glassy phase component. It is have more heating zone compare with U type MoSi2 heater. Moly-D heating elements have the ability to withstand oxidation at high temperatures by forming a protective layer of quartz on its surface. If this glassy phase should be exposed to contaminants, a lower melting phase forms. This material literally drips off the element exposing more molybdenum disilicide on which a new protective oxide layer forms.
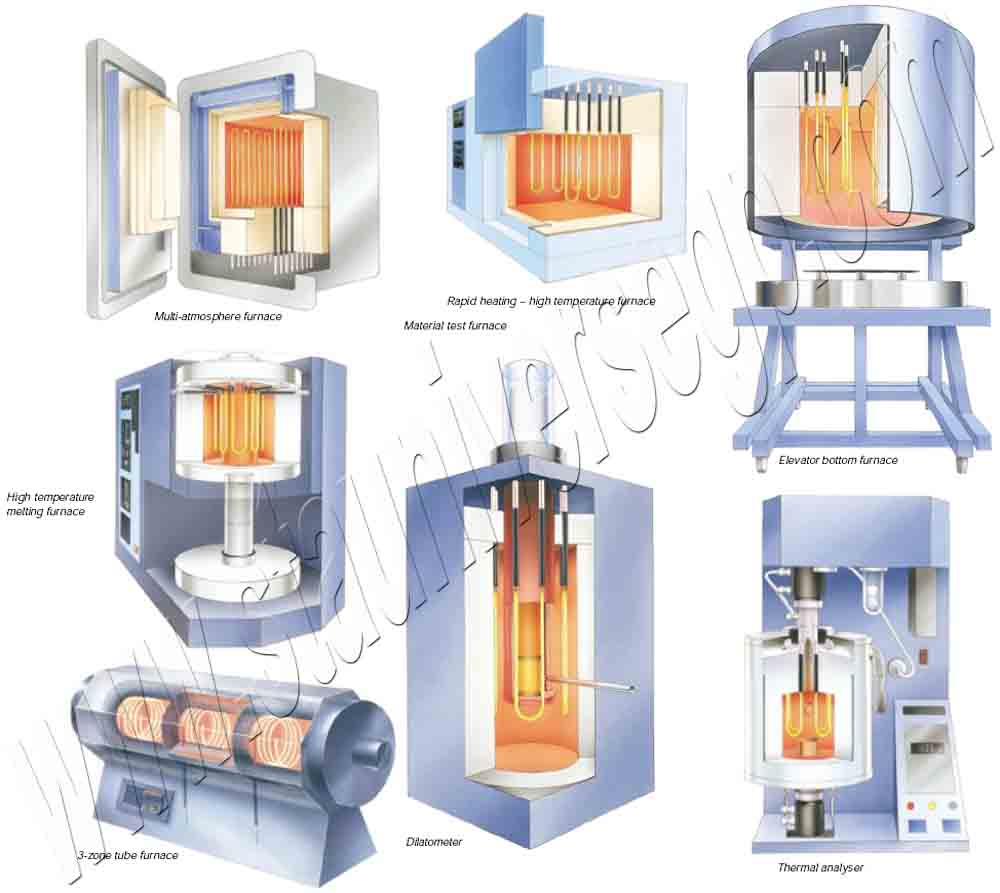
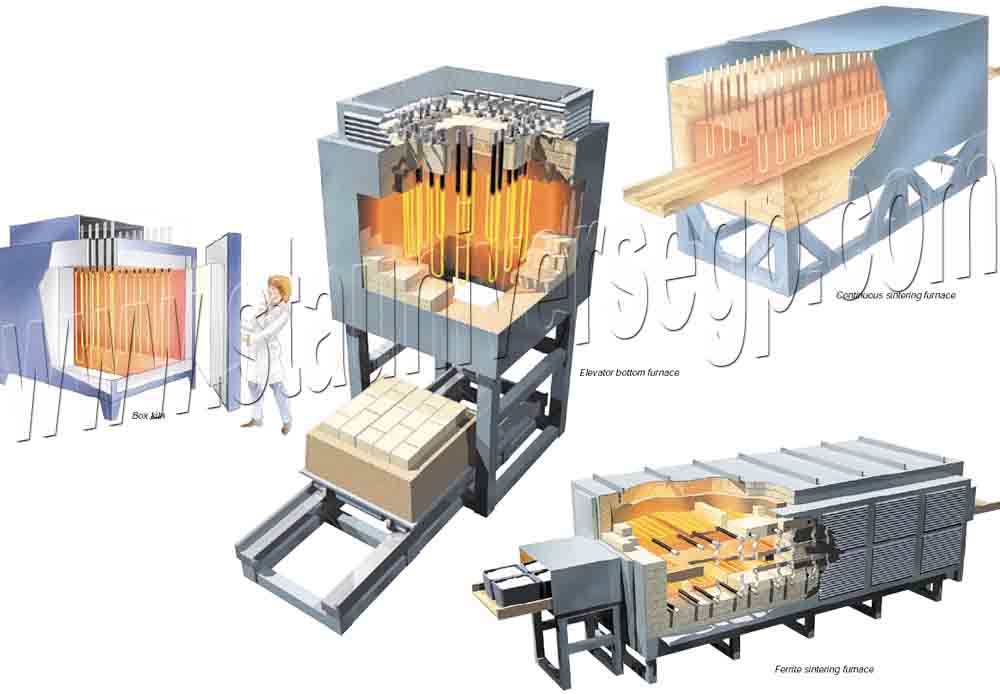
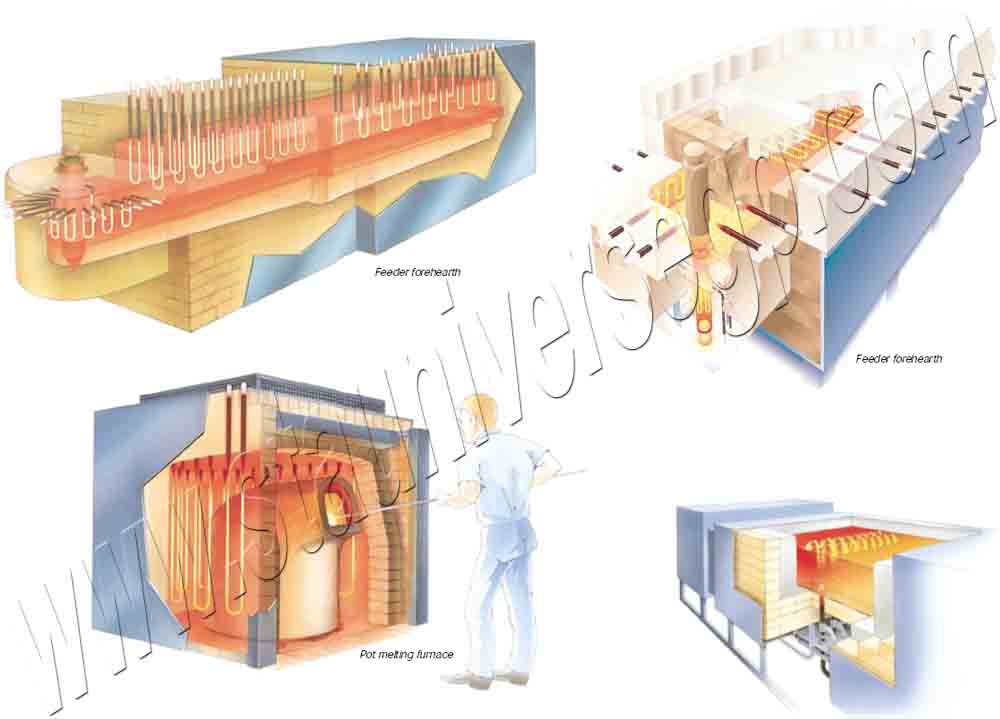
The MoSi2 heating elements have a low specific electrical resistivity with a positive resistance-temperature characteristic. It can be used at a very high watt loading compared to metallic heating elements. Because of its high temperature oxidation resistance, MoSi2 heater electrical resistance remains constant at constant temperature over its useful life. This permits the use of old and new elements together in the same furnace, even if series-connected.

Maximum element temperature depends on the atmosphere within the furnace chamber. In air this is 1800ºC. Since element surface temperature exceeds furnace ambient in relation to the watt loading, careful attention must be given to these parameters for satisfactory element performance.
MoSi2 heating elements normally operate between 1300 and 1850ºC. MoSi2 heater may be used below 1300ºC particularly for furnace atmospheres harmful to silicon carbide heating elements (e.g., sulfur dioxide, water-steam, etc.). Molybdenum disilicide heating elements should not be used between the temperature range of 400 and 700ºC, where a destructive low temperature oxidation may occur called pest.
The Multi-Shank MoSi2 heating element is a dense cermet material consisting of MoSi2 and an oxide, glassy phase component. It is have more heating zone compare with U type MoSi2 heater. Moly-D heating elements have the ability to withstand oxidation at high temperatures by forming a protective layer of quartz on its surface. If this glassy phase should be exposed to contaminants, a lower melting phase forms. This material literally drips off the element exposing more molybdenum disilicide on which a new protective oxide layer forms.
The MoSi2 heating elements have a low specific electrical resistivity with a positive resistance-temperature characteristic. It can be used at a very high watt loading compared to metallic heating elements. Because of its high temperature oxidation resistance, MoSi2 heater electrical resistance remains constant at constant temperature over its useful life. This permits the use of old and new elements together in the same furnace, even if series-connected.


Maximum element temperature depends on the atmosphere within the furnace chamber. In air this is 1800ºC. Since element surface temperature exceeds furnace ambient in relation to the watt loading, careful attention must be given to these parameters for satisfactory element performance.
MoSi2 heating elements normally operate between 1300 and 1850ºC. MoSi2 heater may be used below 1300ºC particularly for furnace atmospheres harmful to silicon carbide heating elements (e.g., sulfur dioxide, water-steam, etc.). Molybdenum disilicide heating elements should not be used between the temperature range of 400 and 700ºC, where a destructive low temperature oxidation may occur called pest.



