Special Shape Moly-D Elements is also usually used in heating modules together with vacuum formed ceramic fiber. This special shape MoSi2 heater can supplied a good temperature for electric furnace, from element temperature 50 to 1800°C, and atmospheres.
Special Shape Moly-D Elements is also usually used in heating modules together with vacuum formed ceramic fiber. This special shape MoSi2 heater can supplied a good temperature for electric furnace, from element temperature 50 to 1800°C, and atmospheres. The long service life and consistent performance of molybdenum disilicide heating elements is due to our emphasis on quality control, from starting material to finished product. Our highly experienced engineers will provide you with expert design necessary for achieving the highest production efficiency at the lowest long-term cost. STA MoSi2 heating elements include 1700, 1800 and 1900 three grade.
STA Moly-D Elements is a high temperature heater, designed for maximum operating temperatures in the 1500-1900 deg C range and for operation in air, so Molybdenum disilicide heating elements are used because of their ability to quickly attain and sustain high temperatures and their affinity for oxidizing atmospheres. Despite their robust appearance they are a fragile, glasslike material with low mechanical shock resistance. Basically, the molybdenum core is coated with quartz glass. The MoSi2 heater become nearly liquid as they approach the maximum temperature, and the glass surface reacts with the oxygen in the air atmosphere to form a renewed coating of protective glass on the element surface.
The maximum MoSi2 heating elements temperature is always 100 deg C higher than the maximum rated furnace temperature, so for example we use 1800 deg C elements in our 1700 deg C furnaces.
The Molybdenum disilicide Heating Elements is a dense cermet material consisting of MoSi2 and an oxide, glassy phase component.
Moly-D elements have the ability to withstand oxidation at high temperatures by forming a protective layer of quartz on its surface. If this glassy phase should be exposed to contaminants, a lower melting phase forms. This material literally drips off the element exposing more molybdenum disilicide on which a new protective oxide layer forms.
Unique Properties of MoSi2 heating elements
MoSi2 heater may be used up to a surface temperature of 1800ºC in oxidizing atmospheres.
Long service life and ease of replacement contribute to high furnace utilization and low maintenance costs.
New and old elements can be used together and in series.
Can dissipate high power loading.
Can be used continuously or intermittently.
Provide rapid furnace temperature ramping.
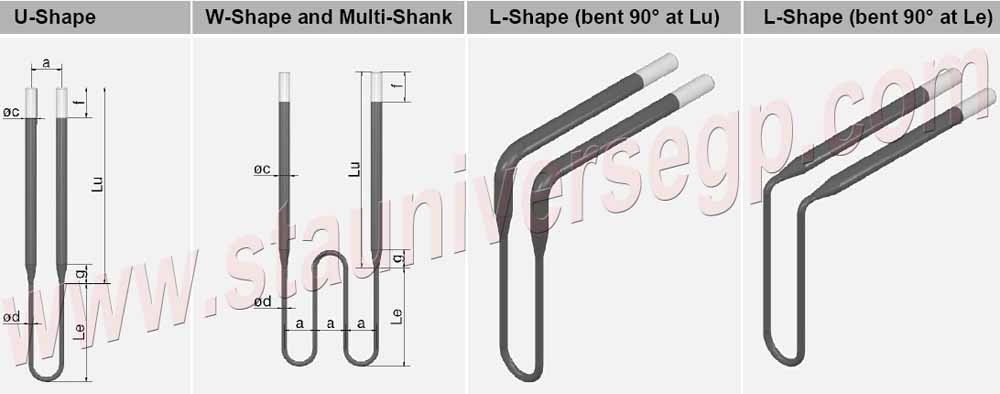

The Moly-D Elements has a low specific electrical resistivity with a positive resistance-temperature characteristic. It can be used at a very high watt loading compared to metallic heating elements. Because of its high temperature oxidation resistance, MoSi2 heater electrical resistance remains constant at constant temperature over its useful life. This permits the use of old and new elements together in the same furnace, even if series-connected.
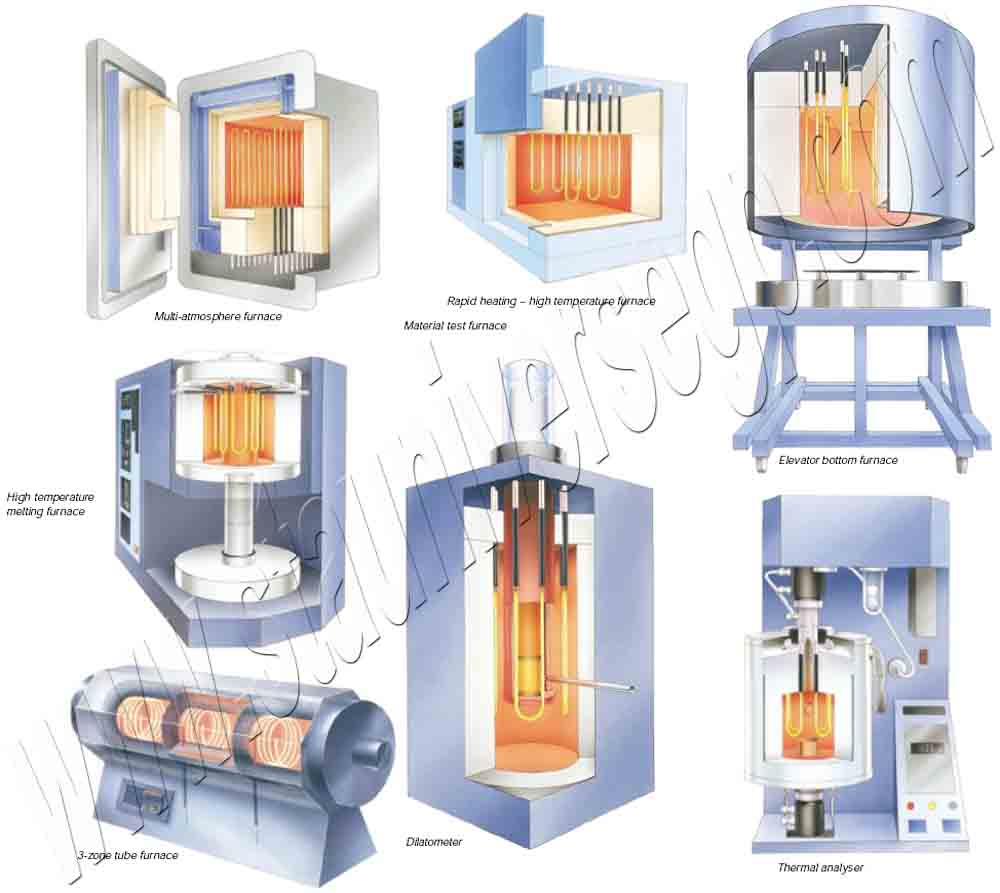
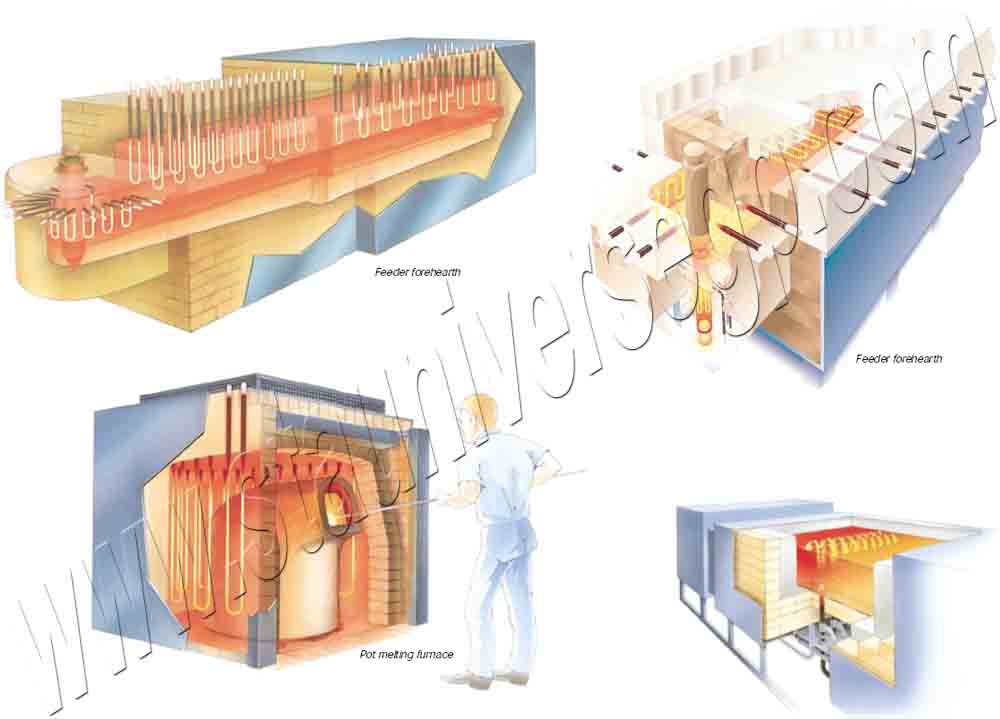
Special Shape Moly-D Elements is also usually used in heating modules together with vacuum formed ceramic fiber. This special shape MoSi2 heater can supplied a good temperature for electric furnace, from element temperature 50 to 1800°C, and atmospheres. The long service life and consistent performance of molybdenum disilicide heating elements is due to our emphasis on quality control, from starting material to finished product. Our highly experienced engineers will provide you with expert design necessary for achieving the highest production efficiency at the lowest long-term cost. STA MoSi2 heating elements include 1700, 1800 and 1900 three grade.
STA Moly-D Elements is a high temperature heater, designed for maximum operating temperatures in the 1500-1900 deg C range and for operation in air, so Molybdenum disilicide heating elements are used because of their ability to quickly attain and sustain high temperatures and their affinity for oxidizing atmospheres. Despite their robust appearance they are a fragile, glasslike material with low mechanical shock resistance. Basically, the molybdenum core is coated with quartz glass. The MoSi2 heater become nearly liquid as they approach the maximum temperature, and the glass surface reacts with the oxygen in the air atmosphere to form a renewed coating of protective glass on the element surface.
The maximum MoSi2 heating elements temperature is always 100 deg C higher than the maximum rated furnace temperature, so for example we use 1800 deg C elements in our 1700 deg C furnaces.
The Molybdenum disilicide Heating Elements is a dense cermet material consisting of MoSi2 and an oxide, glassy phase component.
Moly-D elements have the ability to withstand oxidation at high temperatures by forming a protective layer of quartz on its surface. If this glassy phase should be exposed to contaminants, a lower melting phase forms. This material literally drips off the element exposing more molybdenum disilicide on which a new protective oxide layer forms.
Unique Properties of MoSi2 heating elements
MoSi2 heater may be used up to a surface temperature of 1800ºC in oxidizing atmospheres.
Long service life and ease of replacement contribute to high furnace utilization and low maintenance costs.
New and old elements can be used together and in series.
Can dissipate high power loading.
Can be used continuously or intermittently.
Provide rapid furnace temperature ramping.


The Moly-D Elements has a low specific electrical resistivity with a positive resistance-temperature characteristic. It can be used at a very high watt loading compared to metallic heating elements. Because of its high temperature oxidation resistance, MoSi2 heater electrical resistance remains constant at constant temperature over its useful life. This permits the use of old and new elements together in the same furnace, even if series-connected.


